Tracing the Maritime Silk Road Through Indonesian Ports offers a fascinating glimpse into the rich tapestry of trade and cultural exchange that has shaped Indonesia’s history. This maritime route was not just a path for merchants; it served as a bridge connecting diverse communities, fostering interactions that transformed local economies and societies. As we explore the significance of Indonesian ports in this historical context, we uncover how they played pivotal roles in the global trade network, influencing both local traditions and foreign cultures.
The Maritime Silk Road thrived through bustling ports like Sunda Kelapa, Makassar, and Semarang, which became vital hubs for traders from around the world. These ports facilitated not just the exchange of goods like spices, textiles, and precious metals but also the transfer of ideas and cultural practices, ultimately weaving Indonesia into the larger narrative of maritime history.
Welcome, dear readers! Today, we’re diving deep into the fascinating world of anthropology, a discipline that allows us to explore the intricate tapestry of human culture. Whether you’re an avid learner or just curious, you’re in for a treat as we unravel the stories of our shared humanity.
What is Anthropology?
At its core, anthropology is the study of humans, our ancestors, and our behaviors. It encompasses various subfields, including cultural anthropology, archaeology, linguistic anthropology, and biological anthropology. Each branch contributes a unique perspective, allowing us to understand how cultures evolve and interact, how languages shape societies, and how our biological makeup connects us to our past.
The Four Subfields of Anthropology: Tracing The Maritime Silk Road Through Indonesian Ports
Let’s break down these four main pillars of anthropology, shall we?
Cultural Anthropology
Cultural anthropology focuses on the social lives of living communities. This subfield examines cultural norms, values, practices, and the myriad ways in which culture influences our perceptions and interactions. Cultural anthropologists often engage in ethnographic research, immersing themselves in communities to gain firsthand insights. For example, consider the fascinating traditions of the Maasai people in East Africa, known for their distinctive customs, vibrant dress, and deep connection to their land. By understanding their way of life, we gain a broader perspective on diverse human experiences.
Archaeology
Next up is archaeology, the study of past human societies through their material remains. This subfield provides a glimpse into the lives of ancient peoples, from their tools and pottery to their architectural marvels. Archaeologists use a variety of methods, including excavation and analysis of artifacts, to reconstruct historical narratives. Take the ancient city of Pompeii, for instance; buried under volcanic ash, it has offered remarkable insights into Roman life, from everyday activities to social hierarchies. Through archaeology, we connect with our ancestors and understand the long arc of human history.
Linguistic Anthropology
Linguistic anthropology examines the role of language in shaping human experience. Language is not just a means of communication; it’s a vessel of culture, identity, and social dynamics. This subfield explores how language influences thought, reflects societal norms, and varies across cultures. For instance, consider how the use of honorifics in Japanese signifies respect and social hierarchy. By studying language, linguistic anthropologists uncover deeper meanings behind words and phrases, illuminating the interplay between language and culture.
Biological Anthropology, Tracing the Maritime Silk Road Through Indonesian Ports
Finally, we have biological anthropology, which focuses on the biological aspects of humans, including evolution, genetics, and primate behavior. This subfield examines how our bodies have adapted over time and how our evolutionary history shapes our present. Research in biological anthropology can reveal fascinating information about our ancestors’ lifestyles and environments. For example, the study of Neanderthal remains has shed light on human evolution and our genetic connections to these ancient relatives.
Why Anthropology Matters
You might be wondering, why should we care about anthropology? Well, understanding human culture is crucial in an increasingly globalized world. Anthropology fosters empathy and appreciation for diversity by highlighting the richness of varying customs, beliefs, and practices. In a time when misunderstandings can lead to conflict, anthropology encourages dialogue and connection across cultural divides.
Moreover, anthropological insights can inform contemporary issues, from social justice movements to environmental sustainability. By examining how different communities interact with their environment, anthropologists can contribute valuable knowledge to address pressing global challenges. For instance, indigenous practices in land management often hold key lessons for sustainable agriculture and conservation efforts.
Anthropology in Everyday Life
Anthropology isn’t just an academic pursuit; it’s woven into the fabric of our daily lives. Think about the different cultural practices you encounter regularly, from food traditions to holiday celebrations. Each aspect of your daily experience is shaped by cultural norms and values that have evolved over time.
Take food, for example. The way we prepare, share, and enjoy meals is deeply tied to our cultural heritage. In Italy, for instance, communal dining is an integral part of family life, reflecting a culture that prioritizes relationships and togetherness. In contrast, fast-paced dining in modern urban settings often emphasizes efficiency and convenience. By understanding these differences, we can appreciate the diverse culinary practices that enrich our lives.
The Future of Anthropology
As we look to the future, anthropology continues to evolve. With advancements in technology, researchers can now utilize digital tools to document and analyze cultures in unprecedented ways. Virtual reality, for instance, allows anthropologists to recreate historical sites, providing immersive experiences that engage audiences in new manners.
Additionally, the ongoing challenges posed by globalization, climate change, and migration call for anthropological insights more than ever. By studying how cultures adapt and respond to these changes, anthropologists can help create strategies for resilience and sustainability in our interconnected world.
Conclusion: Embracing the Journey
In conclusion, anthropology invites us to embark on a journey of discovery about ourselves and one another. It enables us to appreciate the rich diversity of human experiences while acknowledging the common threads that unite us. So, whether you’re exploring your own cultural roots or learning about distant communities, remember that anthropology is always there, offering a lens through which we can better understand the human experience.
Thank you for joining me in this exploration of anthropology today! I hope you found it enlightening and engaging. Until next time, embrace the beauty of our shared humanity, and keep asking questions!
FAQ Insights
What was the Maritime Silk Road?
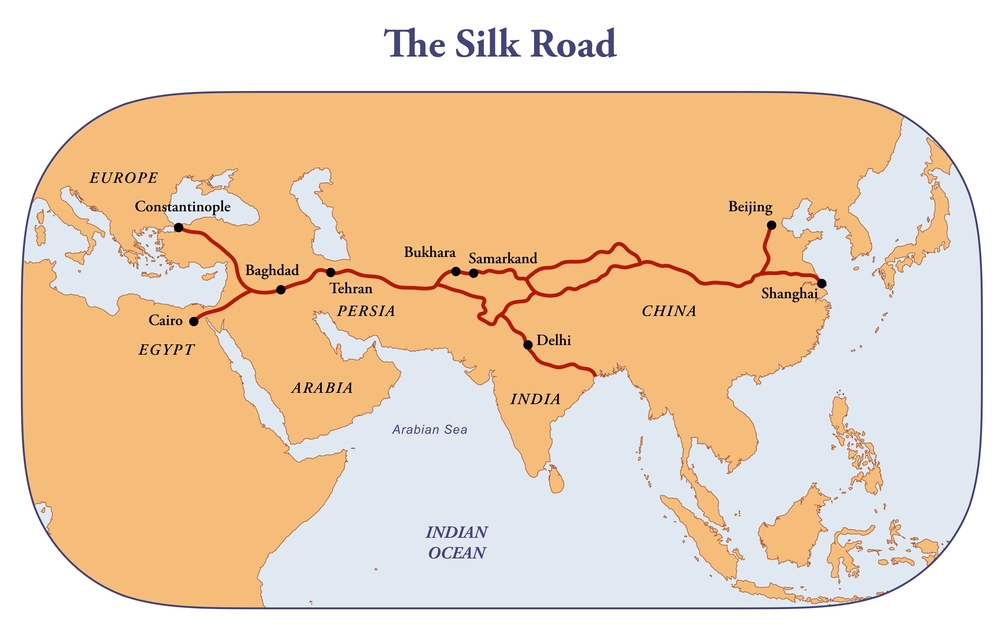
The Maritime Silk Road was a network of sea routes used for trade between Asia, the Middle East, and Europe, facilitating the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas.
Why are Indonesian ports significant to the Maritime Silk Road?
Indonesian ports were crucial trade hubs that connected various cultures and facilitated the exchange of valuable commodities, helping to integrate Indonesia into the global economy.
What types of goods were traded along the Maritime Silk Road through Indonesia?
Goods such as spices, textiles, precious metals, and ceramics were commonly traded along the Maritime Silk Road through Indonesian ports.
How did cultural exchange occur along the Maritime Silk Road?
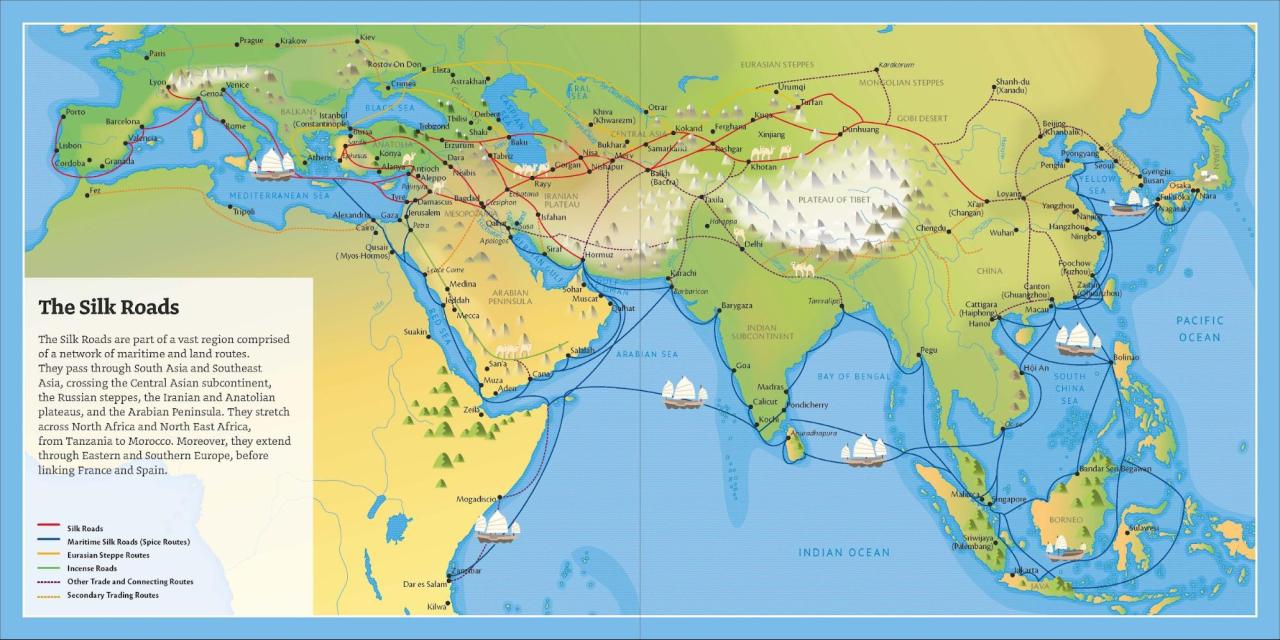
Cultural exchange happened through interactions among traders, leading to the sharing of languages, religions, art, and customs among diverse communities.
What legacy has the Maritime Silk Road left on Indonesia?
The Maritime Silk Road has left a lasting legacy on Indonesia, influencing its cultural diversity, economic development, and international relations throughout history.
Tinggalkan Balasan